HDD vs. SSD
Hard Disk Drives (HDD) were the most used drives by home users as well as corporate users. As and when the storage started being a concern for a single user usage, alternative storage is found.

In the 1990s and early 2000, 500GB of data storage was enough for desktop PCs and laptops. Gradually, video content and game usage started demanding more data storage. 1TB of data has become the minimum storage drive for an individual user.
HDD working mechanism is not enhanced as per the rapid growth we have seen in the data consumption and storage of the users.
Solid State Drive (SSD) has taken the place of traditional Hard Disk Drive (HDD). SSDs are more powerful in terms of speed and storage. Their storage capacity and read-write of data are more efficient than HDDs.
Nowadays, the companies have turned to manufacture hybrid drives that are called SSHD, combination features of both types of drives.
Let us understand the differences between HDD and SSD.
HDD Working Mechanism
The below picture depicts a physical view of a Hard Disk Drive with the parts name mentioned.
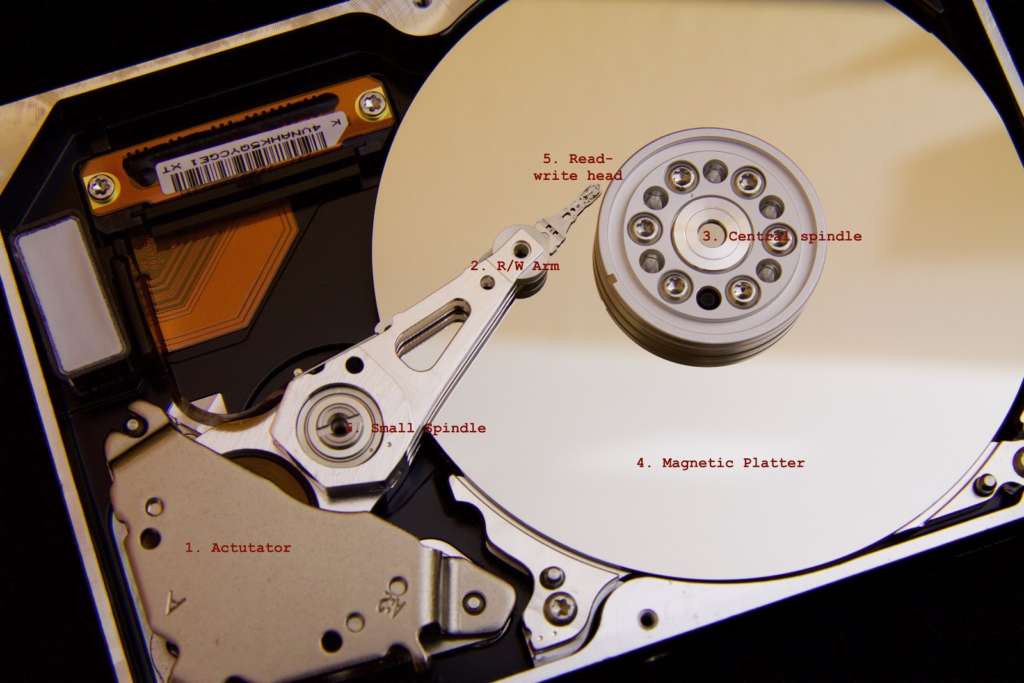

- Actuator – it manages the read-write arm and is responsible for moving the read-write arm quickly and placing them precisely.
- Read-Write Arm – the read-write arm moves the head in the back and forth directly on the magnetic platter. This movement is the process of storing the data.
- Central Spindle – it is responsible for rotating the magnetic platter.
- Magnetic Platter – it stores data in binary form. It rotates at the speed of 5400 RPM to 7200 RPM on laptops and goes to 10000 RPM on desktops.
- Read-Write Head – it is located at the top of the read-write arm and controlled by it.
SSD Working Mechanism
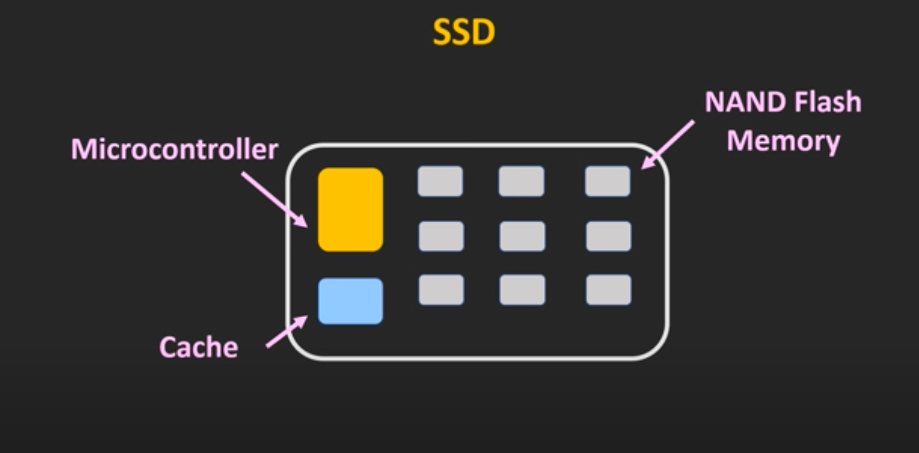
SSDs are designed using the flash memory called NAND. The technology is formed based on non-volatile storage. Non-volatile storage refers to the data retaining without power usage. The data is stored as blocks and it uses electric circuits to store the data when attached with power. Once the power is turned off, it uses the metal oxide semiconductor to keep the data.
Differences between HDD and SSD

Below are the differences listed based on the features of HDDs and SSDs.
| Hard Disk Drive (HDD) | Solid State Drive (SSD) |
| Volatile mechanism – It does not retain data without power. | Non-volatile mechanism – It does not need the power to retain data |
| Weight – It is heavy in weight as compared to an SSD. It uses a metal platter and other parts made up of metal. | Weight – It is lightweight and looks like a RAM chip – sleek in design and very light in weight. |
| Size – For desktops, it comes with 3.5 inches whereas, for laptops, it comes with 2.5 inches. | Size – It comes with 2.5 inches for laptops and desktops. For tablets and other devices, it comes as a chip that is very sleek. |
| Capacity – For desktops/PCs and laptops, the storage capacity available for HDDs ranges from 1TB to 10TB | Capacity – For desktops/PCs and laptops, the storage capacity available for SSDs ranges from 120GB to 4TB |
| Power Consumption – HDD consumes more power as compared to SSD. Chances of damage are more likely in the case of power fluctuation. | Power Consumption – SSD consumes less power compared to HDD. |
Cost
The cost of SSDs is 3-4 times higher than HDDs. Based on the working mechanism and durability, the cost is higher. If you are using desktop PCs and you are not a high-end data consumer, you can choose HDDs. But, if your content/data storage type is video/audio/images with high-resolution files, it is recommended to use SSD.
Speed and Performance
HDDs – Read-Write speed is around 100 Mbps. System boot time and opening of any applications are slower compared to SSDs. The drive stores data in the form of sectors and blocks, the speed is not higher.
SSD – Read-Write speed is around 500mbps. If you have an SSD installed on your desktop/laptop, it quickly boots the system and opens the application. Storing mechanism is in flash chips which increases read-write speed. You can make out a clear difference in the speed and performance of SSD.
Durability and Age
As HDDs read-write of data is done by spinning the headers on the metal platter. This mechanism has limits in terms of durability. There are chances of a read-write head deteriorating based on the usage. SSDs do not have a part similar to a metal head that spins in the case of HDDs. They have memory blocks in which the data is stored. No process is active once you detach the SSD from the system.
Noise
HDDs when in use, produce noise. The faster hard drive produces more noise. If the writing speed of the HDD is above 10000RPM, it will make more noise while working with data. SSDs make no noise at all as their working mechanism is non-mechanical. HDDs lead to more power consumption than SSDs. As a result, billing and maintenance are higher in HDDs.
Top 4 HDDs
Based on the windows central survey, the following are the top HDDs available in 2020.
Seagate FireCuda 2TB internal hard drive
- SSHD – A hybrid form of the drive (mix of HDD and SSD)
- Speed – 7,200 RPM
- Storage – 2TB/3TB
- Make – SATA 6gbps
- Cost – low cost
For more information, visit https://www.windowscentral.com/best-internal-hard-drives website.
Western Digital Black
- Speed – 10,000 RPM
- Storage – 2TB
- Warranty – 5year warranty
- Cost – low cost
For more information, visit https://www.windowscentral.com/best-internal-hard-drives website.
Seagate BarraCuda 2TB solid state hybrid drive
- Speed – 7,200 RPM
- Storage – 1TB to 8TB
- Warranty – 2year warranty
- Cost – low cost
Seagate IronWolf
- Speed – 5,900 RPM
- Storage – 1TB to 2TB
- Warranty – 3year warranty
- Cost – low cost
For more information, visit https://www.windowscentral.com/best-internal-hard-drives website.
Top 4 SSDs
PC Magazine’s reviews and ratings for the top 4 SSDs are as below.
ADATA XPG Spectrix S40G
- 1TB storage
- 4K write and sequential read-outputs
- $149 in price
- Most used by gamers
For more information, visit the https://in.pcmag.com/ssd/135184/adata-xpg-spectrix-s40g website.
Crucial P5
- 4K write and read performance
- 5-year warranty
- Better durability
- Good price-to-performance ratio
For more information, visit the https://in.pcmag.com/ssd/137549/crucial-p5 website.
Seagate FireCuda 510
- Fast and speedy performance
- Highly durable
- Competitive price
For more information, visit the https://in.pcmag.com/ssd/130726/seagate-firecuda-510 website.
Samsung SSD 870 QVO
- SATA based SSD
- 2TB storage (4TB is coming out soon)
- 4K read and write speed
- Excellent price-to-performance ratio
For more information, visit the https://in.pcmag.com/ssd/136947/samsung-ssd-870-qvo website.
Takeaway
You can decide to choose your storage option based on your priority on the features they provide. If noise, form factor, and performance are your primary needs, SSD is your choice. If higher capacity and price are your choice, HDD can be selected by you.

